| The World Bank
Group. Global Development Finance 1998 Debt
indicators
The macroeconomic aggregates and debt data provided in the tables
are used to generate ratios that analysts use to assess the external situations of
developing countries. Different analysts give different weights to these indicators, but
no single indicator or set of indicators can substitute for a thorough analysis of the
overall situation of an economy. The advantage of the indicators in Global Development
Finance is that they are calculated from standardized data series that are compiled on
a consistent basis by the World Bank and the IMF. The ratios offer various measures of the
cost of, or capacity for, servicing debt in terms of the foreign exchange or output
forgone. The following ratios are provided based on total external debt:
EDT/XGS is total external debt to exports of goods and
services (including workers’ remittances).
EDT/GNP is total external debt to gross national product.
TDS/XGS, also called the debt service ratio, is total debt
service to exports of goods and services (including workers’ remittances).
INT/XGS, also called the interest service ratio, is total
interest payments to exports of goods and services (including workers’ remittances).
INT/GNP is total interest payments to gross national
product.
RES/EDT is international reserves to total external debt.
RES/MGS is international reserves to imports of goods and
services.
Short-term/EDT is short-term debt to total external debt.
Concessional/EDT is concessional debt to total external
debt.
Multilateral/EDT is multilateral debt to total external
debt.
Back to top
Back to Contents
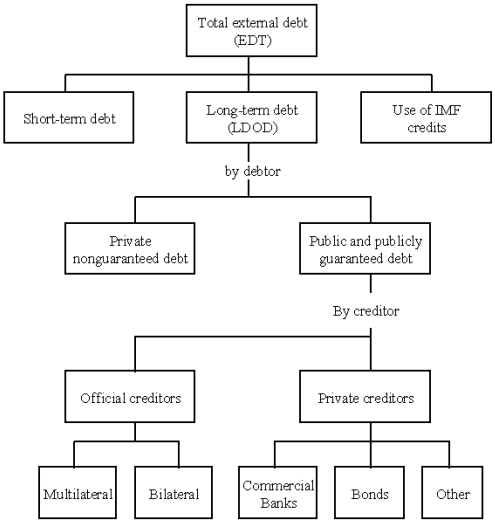
Long-term debt
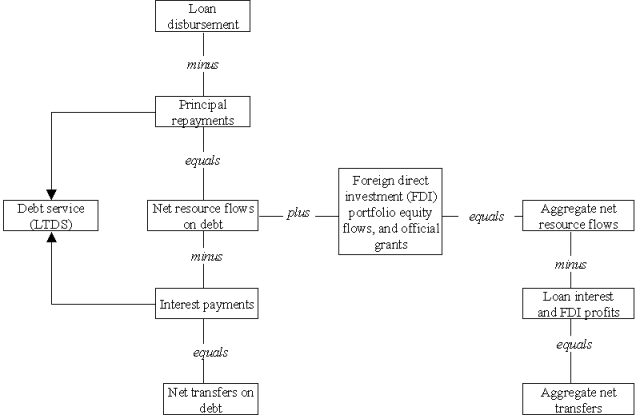
Data on long-term debt include eight main elements:
DEBT OUTSTANDING AND DISBURSED is the
total outstanding debt at year end.
DISBURSEMENTS are drawings on loan
commitments by the borrower during the year.
PRINCIPAL REPAYMENTS are amounts paid by
the borrower during the year.
NET FLOWS received by the borrower during
the year are disbursements minus principal repayments.
INTEREST PAYMENTS are amounts paid by the
borrower during the year.
NET TRANSFERS are net flows minus interest
payments during the year; negative transfers show net transfers made by the borrower to
the creditor during the year.
DEBT SERVICE (LTDS)
is the sum of principal repayments and interest payments actually made.
UNDISBURSED DEBT is total debt undrawn at
year end; data for private nonguaranteed debt are not available.
Data from individual reporters are aggregated by type of
creditor. Official creditors includes multilateral and bilateral debt.
• Loans from multilateral organizations are
loans and credits from the World Bank, regional development banks, and other multilateral
and intergovernmental agencies. Excluded are loans from funds administered by an
international organization on behalf of a single donor government; these are classified as
loans from governments.
• Bilateral loans are loans from governments and
their agencies (including central banks), loans from autonomous bodies, and direct loans
from official export credit agencies.
Private creditors include bonds, commercial banks, and
other private creditors. Commercial banks and other private creditors comprise bank and
trade-related lending.
• Bonds include publicly issued or privately
placed bonds.
• Commercial banks are loans from private banks
and other private financial institutions.
• Other private includes credits from
manufacturers, exporters, and other suppliers of goods, and bank credits covered by a
guarantee of an export credit agency.
Four characteristics of a country’s debt are given as
memorandum items for long-term debt outstanding and disbursed (LDOD).
Concessional LDOD conveys information about the
borrower’s receipt of aid from official lenders at concessional terms as defined by
the DAC, that is, loans with an original grant element of 25 percent or more. Loans from
major regional development banks—African Development Bank, Asian Development Bank,
and the Inter-American Development Bank—and from the World Bank are classified as
concessional according to each institution’s classification and not according to the
DAC definition, as was the practice in earlier reports.
Variable interest rate LDOD is long-term debt with
interest rates that float with movements in a key market rate such as the London interbank
offer rate (LIBOR) or the U.S. prime rate. This item conveys information about the
borrower’s exposure to changes in international interest rates.
Public sector LDOD and private sector LDOD convey
information about the distribution of long-term debt for DRS countries by type of debtor
(central government, state and local government, central bank; private bank, private
debt).
Back to top
Back to Contents
Currency
composition of long-term debt
The six major currencies in which the external debt of low- and
middle-income countries is contracted are separately identified, as is debt denominated in
special drawing rights and debt repayable in multiple currencies.
Debt restructurings
Debt restructurings include restructurings in the context of the
Paris Club, commercial banks, debt-equity swaps, buybacks, and bond exchanges. Debt
restructuring data capture the noncash or inferred flows associated with rescheduling and
restructuring. These are presented to complement the cash-basis transactions recorded in
the main body of the data.
Debt stock rescheduled is the amount of debt outstanding
rescheduled in any given year.
Principal rescheduled is the amount of principal due or in
arrears that was rescheduled in any given year.
Interest rescheduled is the amount of interest due or in
arrears that was rescheduled in any given year.
Debt forgiven is the amount of principal due or in arrears
that was written off or forgiven in any given year.
Interest forgiven is the amount of interest due or in
arrears that was written off or forgiven in any given year.
Debt stock reduction is the amount that has been netted
out of the stock of debt using debt conversion schemes such as buybacks and equity swaps
or the discounted value of long-term bonds that were issued in exchange for outstanding
debt.
Debt stock-flow
reconciliation
Stock and flow data on total external debt are reconciled for
each year, beginning with 1989. The data show the changes in stock that have taken place
due to the net flow on debt, the net change in interest arrears, the capitalization of
interest, the reduction in debt resulting from debt forgiveness or other debt reduction
mechanisms, and the cross-currency valuation effects. The residual difference—the
change in stock not explained by any of these factors—is also presented, calculated
as the sum of identified accounts minus the change in stock.
Average terms
of new commitments
The average terms of borrowing on public and publicly guaranteed
debt are given for all new loans contracted during the year and separately for loans from
official and private creditors. To obtain averages, the interest rates, maturities, and
grace periods in each category have been weighted by the amounts of the loans. The grant
equivalent of a loan is its commitment (present) value, less the discounted present value
of its contractual debt service; conventionally, future service payments are discounted at
10 percent. The grant element of a loan is the grant equivalent expressed as a percentage
of the amount committed. It is used as a measure of the overall cost of borrowing. Loans
with an original grant element of 25 percent or more are defined as concessional. The
average grant element has been weighted by the amounts of the loans.
Commitments cover the total amount of loans for which contracts
were signed in the year specified; data for private nonguaranteed debt are not available.
Projections on
existing pipeline
Projected debt service payments are estimates of payments
due on existing debt outstanding, including undisbursed. They do not include service
payments that may become due as a result of new loans contracted in subsequent years. Nor
do they allow for effects on service payments of changes in repayment patterns owing to
prepayment of loans or to rescheduling or refinancing, including repayment of outstanding
arrears, that occurred after the last year of reported data.
Projected disbursements are estimates of drawings of
unutilized balances. The projections do not take into account future borrowing by the
debtor country. See Methodology section for a detailed explanation of the methods of
projecting undisbursed balances.
Back to top
Back to Contents
Exchange rates
Data received by the World Bank from its members are expressed in
the currencies in which the debts are repayable or in which the transactions took place.
For aggregation, the Bank converts these amounts to U.S. dollars using the IMF par values
or central rates, or the current market rates where appropriate. Service payments,
commitments, and disbursements (flows) are converted to U.S. dollars at the average rate
for the year. Debt outstanding and disbursed at the end of a given year (a stock) is
converted at the rate in effect at the end of that year. Projected debt service, however,
is converted to U.S. dollars at rates in effect at end-December 1996. Debt repayable in
multiple currencies, goods, or services and debt with a provision for maintenance of value
of the currency of repayment are shown at book value.
Adjustments
Year-to-year changes in debt outstanding and disbursed are
sometimes not equal to net flows; similarly, changes in debt outstanding, including
undisbursed, differ from commitments less repayments. The reasons for these differences
are cancellations, adjustments caused by the use of different exchange rates, and the
rescheduling of other liabilities into long-term public debt.
Symbols
The following symbols have been used throughout:
0.0 indicates that a datum exists, but is negligible, or is a
true zero.
.. indicates that a datum is not available.
Dollars are current U.S. dollars unless otherwise specified.
Back to top
Back to Contents
Aggregate net resource flows and net transfers (long-term) to
developing countries
Back to top
Back to Contents
| |
Credits |
Debits |
|
Current account |
- Exports of goods and services
|
Imports of goods and services
|
|
|
Income paid
|
- Current transfers including workers' remittances and private grants
|
|
- Official unrequited transfers (by foreign governments
|
Official unrequited transfers (by national government)
|
Capital and financial account |
- Official unrequited transfers (by foreign governments)
|
Official unrequited transfers (by national government)
|
- Foreign direct investment (by nonresidents) (disinvestment shown as negative)
|
Foreign direct investment (by residents) (disinvestment shown as negative)
|
- Portfolio investment (by nonresidents) (amortization shown as negative)
|
Portfolio investment (abroad by residents) (amortization shown as negative)
|
- Other long-term capital inflows (by nonresidents) (amortizations shown as negative)
|
Other long-term capital outflow (by residents) (amortizations shown as negative)
|
- Short-term capital inflow
|
Short-term capital outflow
|
Reserve account |
Net changes in reserves |
|
Aggregate net resource flows |
|
Net resource flows on debt (long-term) |
Back to top
Back to Contents |